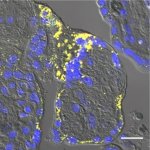
News • Amyloid-β-induced functional placental impairment
Researchers link Alzheimer’s disease protein to preeclampsia
Researchers have discovered that amyloid-β deposits - similar to those found in Alzheimer’s disease - may contribute to the development of preeclampsia during pregnancy.