Article • Screening
Can, should and must MRI replace mammography?
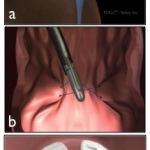
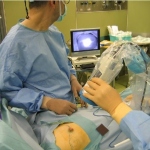
In breast cancer care each patient receives personalised, highly effective diagnosis and treatment procedures. In breast diagnostics this mainly revolves around new MRI scanning procedures that allow the quantification of biological and physiological processes on a cellular and molecular level.