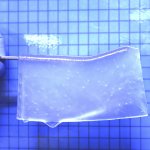
News • Enabling neuronal tissue growth
A hydrogel to heal the brain
Synthetic hydrogels were shown to provide an effective scaffold for neuronal tissue growth in areas of brain damage, providing a possible approach for brain tissue reconstruction.

Synthetic hydrogels were shown to provide an effective scaffold for neuronal tissue growth in areas of brain damage, providing a possible approach for brain tissue reconstruction.

In a recent study, a US research team developed a revolutionary laser-based approach to perform microbiopsies. Their novel method could make biopsies faster, more cost-effective, and less harmful to the patient.
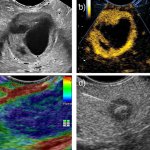
Endosonography poses unique challenges for medical professionals, because two demanding disciplines have to be mastered at the same time. The use of artificial intelligence (AI) could help speed up the notoriously slow learning curve of the procedure, says Prof Dr Christoph F. Dietrich. At the Visceral Medicine Congress in Hamburg, the expert explained how AI can help endosonography achieve…

Histopathology company Sakura Finetek Europe announces the launch of its newest solution Tissue-Tek Genie, an advanced staining system, entering a new market.

A research team has created the first gel-based cartilage substitute that is even stronger and more durable than the real thing, offering a promising solution for patient suffering from knee pain.
A new device, which doesn’t rely on immunosuppressing drugs, may assist efforts to develop an artificial pancreas to treat diabetes.

Researchers have developed 3D printed artificial heart valves designed to allow a patient’s own cells to form new tissue.
Biomaterial engineers have developed the first-ever hydrophobic fluid, which instantly displaces body fluids surrounding an injury allowing for near-instantaneous gelling, sealing, and healing of injured tissue.
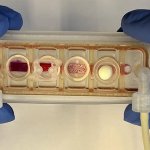
A major advance demonstrates first multi-organ chip made of engineered human tissues linked by vascular flow for improved modeling of systemic diseases like cancer.

An international research team has now found an approach to lower the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and reduce the associated development of liver fibrosis.
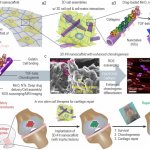
Researchers have established an injectable hybrid inorganic nanoscaffold-templated stem cell assembly and applied it to the regeneration of critically-sized cartilage defects.
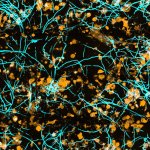
A chip-based infection model developed by Jena researchers enables live microscopic observation of damage to lung tissue caused by the invasive fungal infection aspergillosis.

A proof of concept for a robot that can reach some of the smallest bronchial tubes in the lungs to take tissue samples or deliver cancer therapy.
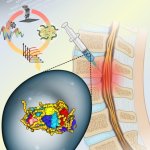
By employing artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics to formulate therapeutic proteins, researchers promoted tissue regeneration.
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) develop a protocol to transplant 3D cellular structures that could regenerate damaged intestine.

Researchers have developed a combination of materials that can morph into various shapes before hardening. The material is initially soft, but later hardens through a bone development process that uses the same materials found in the skeleton.
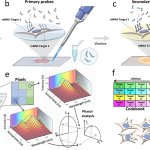
A new biopsy tool will enable scientists and clinicians to simultaneously profile many biomarkers in cells and tissues.
A tiny ‘pop-up’ sensor monitors the electrical activity inside heart cells. The device could provide new insights into cardiac diseases, including myocardial infarction and arrhythmias.
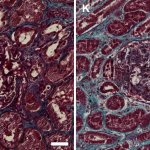
The Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 infects the kidneys and contributes to tissue scarring, as shown by researchers from Germany and the Netherlands.
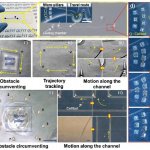
The joint research team of Prof. Hongsoo Choi (DGIST) & Prof. Sung Won Kim (Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital), developed an hNTSC-based microrobot for minimally invasive delivery into the brain tissue via the intranasal pathway.
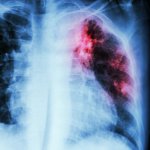
After infection with SARS-CoV-2, where does the immune system store the memory to provide long-term protection against reinfection? Though numerous studies have examined blood to track immune responses to SARS-CoV-2, a new study of Covid survivors shows that the memory of the infection is primarily stored in T and B cells within the lung and the lymph nodes surrounding the lung.
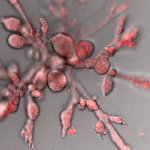
Many of the organ systems found in animals exhibit highly complex structures, which are essential for their various functions. How such structures develop during embryonic development is a central question in biology. Physicists led by Erwin Frey (Professor of Statistical and Biological Physics at LMU Munich) and Andreas Bausch (Professor of Cellular Biophysics at the Technical University of…
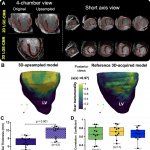
A multidisciplinary team of scientists based at the Universidad de Valladolid and the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) has developed a highly efficient method for identifying the 3-dimensional features of the scar tissue formed after a myocardial infarction. The study was carried out in partnership with scientists and clinicians at Hospital Clínico San Carlos, Hospital…

Imaging company Lumito has secured a European patent for an instrument and staining reagents based on UCNPs (up-converting nanoparticles) for imaging in scattering materials, such as human tissue. The instrument is intended for use in tissue diagnostics, to provide pathologists visual depictions of tissue samples as an input for making diagnosis. The technology is patented across three global…
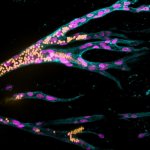
Using lab-created tissue to heal or replace damaged organs is one of the great visions for the future of medicine. Synthetic materials could be suitable as scaffolding for tissue because, unlike natural tissues, they remain stable in the organism long enough for the body to form new natural structures. A fundamental requirement for functional tissue is that blood vessels must be able to grow in…