News • Deep learning advances
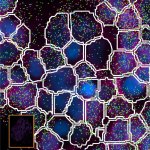
New AI model for cell segmentation and classification
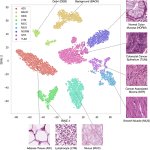
US researchers have developed a comprehensive deep learning AI model designed to more accurately identify and classify cells in high-content tissue images.

US researchers have developed a comprehensive deep learning AI model designed to more accurately identify and classify cells in high-content tissue images.
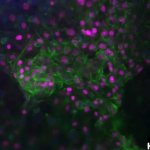
An “out-of-this-world” project has the potential to transform the future of tissue engineering and liver transplantation through research conducted aboard the International Space Station (ISS).

Sakura Finetek’s Tissue-Tek Xpress® x120 Rapid Tissue Processor is the only instrument on the market that allows for continuous, rapid processing of both biopsy and larger tissue, resulting in a streamlined histology workflow. Being part of Sakura’s SMART Automation concept, this tissue processing solution is designed to automate manual work and create a continuous flow throughout the lab.
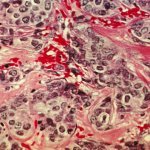
A new study confirms fibrosis as a prognostic indicator in HER2-negative, the most common breast cancer, and opens the way to antifibrotic drug treatments.

Researchers have created a mucus-based bioink which can be used for 3D printing lung tissue. This advance could one day help study and treat chronic lung conditions.
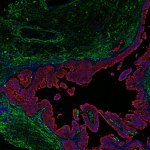
Researchers at Stanford have demonstrated that conditions in the matrix surrounding pancreatic cancer cells impact whether those cells respond to chemotherapy.

Adding a new dimension to pathology: Researchers explore new, deep learning models that can use 3D pathology datasets to make clinical outcome predictions for curated prostate cancer specimens.

Artificial cells to combat cancer: Research groups are working to create synthetic micro-organisms capable of detecting the presence of the disease and delivering anti-cancer therapies.
Researchers have developed the 'iKnife', a smart scalpel that is able to recognise healthy tissue from brain tumour in seconds as it cuts, with more than 98% accuracy.
Patients suffering from cartilage defects in the knee may benefit from a new method in development: Using cartilage from the nose, researchers grow a tailor-made implant.
Cancer patients receiving radiotherapy run the risk of injuring their lungs. This can lead to conditions like pneumonitis and fibrosis. A new cell-by-cell model can help make treatments safer.
Material scientists at TU Wien (Vienna) have developed a new approach to producing artificial cartilage tissue: using a 3D printer, cells are grown in microstructures.

AI models are highly capable in analysing tissue samples – as long as conditions are lab-perfect. Add a little contamination, however, and diagnostic accuracy goes out the window, a new study shows.

A paper published in Trends in Cancer explains the advantages of RENACER, the world’s first repository of brain metastases live samples, created by researchers at CNIO.
Researchers from Finland have developed an artificial intelligence tool for automatic colorectal cancer tissue analysis that outperforms prior methods.
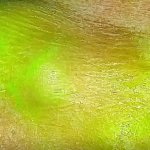
A team of researchers has developed a visualisation tool that combines high-speed cameras and fluorescent injection to distinguish tumour tissue from normal tissue across cancer types.
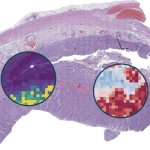
For the first time, researchers show that AI-based predictions can deliver comparable results to clinical tests on biopsies of patients with colorectal cancer (CRC).

Can per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) increase the risk of breast cancer? A new study by US researchers examines the effects of the so-called “forever chemicals”.
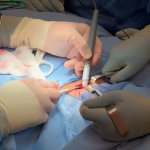
In thyroid removal surgery, reliable discrimination between different tissues is crucial. US surgeons have evaluated how a new handheld device using mass spectrometry can assist them.
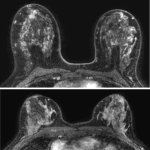
A machine learning model found that background parenchymal enhancement (BPE) on breast MRI is an indicator of breast cancer risk in women with extremely dense breasts.

A research team at UCLA has made an important advancement to address one of the major challenges in cell-free DNA (cfDNA) testing, also known as liquid biopsy.
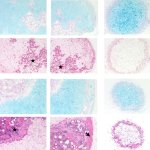
A Japanese research group has developed a method using iPS cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells (iMSC) to create cartilage spheroids, offering new possibilities for tissue repair.

It is crucial that labs can rely on their slides for a seamless – and accurate – diagnosis. With many more commercial instruments focusing on flexibility and choice, these qualities are difficult to separate from subjectivity and complexity.
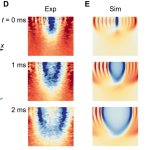
A new ultrasound method that can measure the level of tension in human tissue for the first time - a key indicator of disease - has been developed by researchers from the University of Sheffield.

Researchers at Linköping, Lund, and Gothenburg universities in Sweden have successfully grown electrodes in living tissue using the body’s molecules as triggers.