News • Personalised oncology
New platform to significantly reduce cancer drug testing and screening time
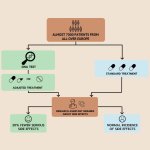
In a breakthrough for personalised oncology, scientists have developed and demonstrated a novel platform that can significantly reduce the time needed to determine the efficacy of anti-cancer drugs.