Image source: LUMC
News • Personalised medicine
DNA-matching medication reduces side effects by 30%
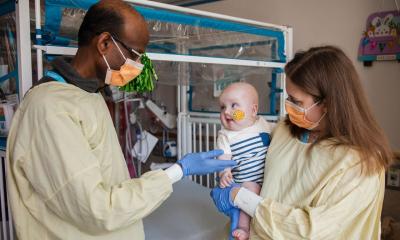
According to an international group of researchers led by Leiden University Medical Center (LUMC), patients experience 30% fewer serious side effects when medication doses are tailored to their DNA.
The study, published in The Lancet, is the first to demonstrate the practical application of prescribing drugs based on an individual’s genetic information.
The ‘one-size-fits all’ approach for prescribing medication is outdated. Due to variations in our genetic information, patients may respond differently to a specific drug. For example, some individuals process medication faster than others and, as a result, require a higher dose to achieve the necessary intervention effect. Personalised treatments are therefore desirable. To facilitate this, researchers developed a ‘DNA medication pass’ that associates a patient’s genetic profile to drugs of which the processing is influenced by DNA. Scanning the pass enables doctors and pharmacists to know what the optimal medication dose is for the individual being treated.
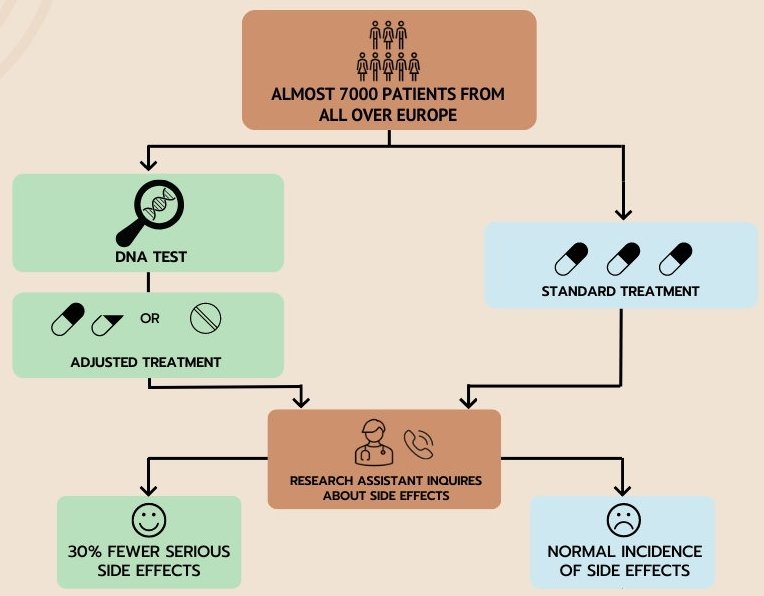
Image source: LUMC
The study found that patients who actively make use of the medication pass, and whose doses are adjusted according to their DNA, experienced 30% fewer serious side effects than patients who were prescribed a standard dose of medication. Approximately 7000 patients from seven European countries were assessed over several medical specialities, including oncology, cardiology, psychiatry and general medicine.
All participants were prescribed a drug the processing of which is influenced by our genes. First, the DNA of each patient was mapped. Researchers then looked at 12 specific genes. 50 types of genetic variants were shown to affect how the 39 selected drugs worked. Up to 12 weeks after initiating treatment, patients were contacted by a nurse specialist who enquired about their side effects, such as diarrhoea, anaemia, nerve pain or loss of taste.

Image source: LUMC
Not only did the ones holding the DNA medication pass experience fewer side effects, but they also expressed great satisfaction with the pass itself. According to the researchers, the pass gives patients the feeling of being more in control, as they become actively involved in their personalised treatment.
The study was coordinated by Henk-Jan Guchelaar, Professor of Clinical Pharmacy at LUMC. He has conducted research in the field of pharmacogenetics for over 20 years. “For the first time we have proven that a ‘tailored’ strategy works at a large scale within clinical practice. There is now enough evidence for us to proceed with implementation,” says Guchelaar. “This means the next step for us is to start making use of the DNA medication pass,” adds Jesse Swen, Professor of Clinical Pharmacy and principal investigator.
Figuring out the subsequent stages of the implementation process also raises various questions for the researchers: Should the pass be reimbursed? And should it be considered part of standard care? Guchelaar and Swen believe it should. According to them, this study provides a good foundation to do so. “We want to move towards mapping the DNA of every patient who comes to the pharmacy,” Guchelaar notes. “In this way, we can make treatment more effective and safer for each patient”.
Source: Leiden University Medical Center
07.02.2023