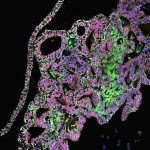
Scientists tissue-engineer part of human stomach
Researchers at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center grew functional stomach and intestinal tissues to study diseases and new drugs. They use pluripotent stem cells to generate human stomach tissues in a petri dish that produce acid and digestive enzymes.