Article • Denmark
Successful digital pathology
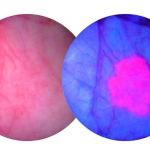
Advanced computer software underpins a service - coupled with a countrywide database, which enables Denmark’s pathologists to optimise the assessment of patients’ specimens.In turn, the digitisation of the system in recent years has led to significant improvements in pathology services, delivering greater efficiency and advances in patient safety.