Article • Gender-specific symptoms
AI pilot project: Early detection of heart attacks in women
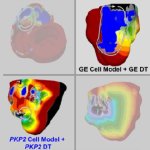
A new research collaboration aims to develop a forward-looking AI application to detect gender-specific symptoms earlier and further reduce mortality from heart disease, especially among women.