News • Soft, wireless implant
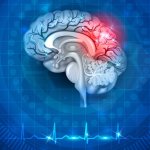
A dissolving cardiac device that monitors and treats heart disease
A new device could monitor and treat heart disease and dysfunction in the days, weeks or months following traumatic heart-related events — and harmlessly dissolve afterwards.