News • Making the invisible visible
New method opens unexplored realms for liquid biopsies
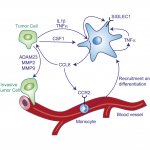
Advancing technology is allowing scientists increasingly to search for tiny signs of cancer and other health issues in samples of patients’ blood and urine. These “liquid biopsies” are less invasive than a traditional biopsy, and can provide information about what’s happening throughout the body instead of just at a single site. Now researchers at the University of Michigan Rogel Cancer…