News • Machine learning analyses driving behaviour
Digital markers offer "near-perfect" dementia prediction
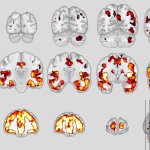
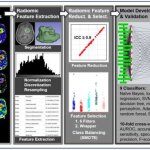
US researchers are developing a highly accurate machine learning model for early detection of mild cognitive impairment and dementia in older drivers.