News • Novel treatment strategy
Antibacterial nanoparticles to shorten tuberculosis therapy duration
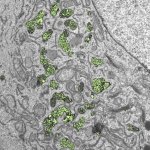
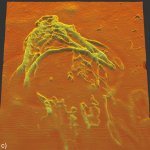
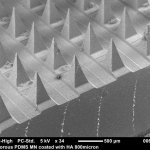
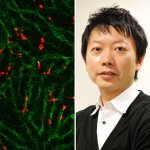
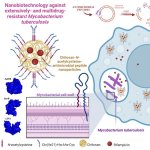
A low-cost technology involving nano-sized antimicrobial compounds against tuberculosis has been developed by researchers at São Paulo State University (UNESP).