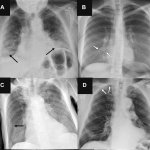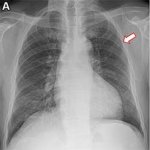
News • Opportunistic screening using chest X-rays
AI identifies non-smokers at high risk for lung cancer
Incidence of lung cancer among people who never smoked is rising. A new AI tool opens the door for opportunistic screening for this group, using existing chest X-rays in the electronic medical record.