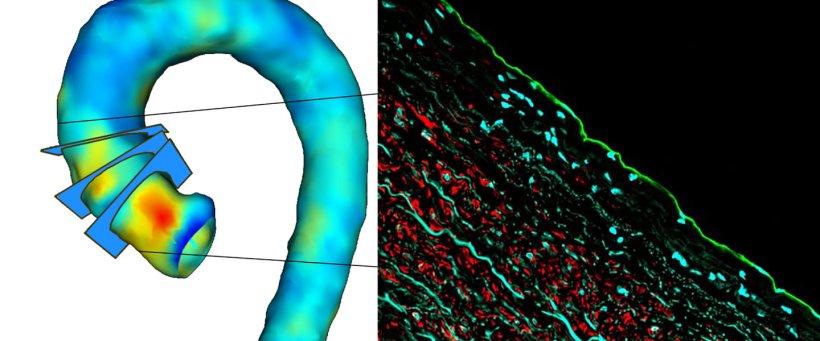
Figures modified from Kiema M et al. Front Physiol. 2022, 7;13:934941 and Johanna Laakkonen group
News • Dissection, rupture, dilatation
Aortic stability assessment to identify high-risk patients
Prediction of aortic dissection or rupture of the thoracic aortic aneurysm is a challenge, and more accurate identification of high-risk patients and timing of repair surgery are required.
A new collaborative study by the University of Eastern Finland and Kuopio University Hospital indicates that magnetic resonance imaging-derived wall shear stress values predict pathological changes in the aortic wall in patients with ascending aortic dilatation. The findings could be used for the identification of high-risk patients in the future. The study is openly accessible in Frontiers in Physiology.
In ascending aortic dilatation, the aorta progressively dilates due to the weakening of the aortic wall structure leading to the formation of an aneurysm. This can lead to severe complications, such as aortic dissection or rupture. The main risk factors for ascending aortic dilatation are the bicuspid aortic valve and certain genetic factors or syndromes. Besides surgical intervention, no effective treatment exists. Typically, patients are asymptomatic, and an aneurysm is discovered incidentally, or only when a life-threatening complication occurs. After diagnosis, aortic dilatation is monitored regularly by computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
Our research aim is to identify novel molecular targets for aortic dilatation that could be used to develop their therapeutics and diagnostics
Johanna Laakkonen
Besides genetics, aortic vascular flow has been suggested to induce changes in the aortic wall structure and to contribute to disease progression. The new study from the University of Eastern Finland and Kuopio University Hospital shows for the first time the relation between wall shear stress, aortic wall strength, and site-specific cell composition in patients having ascending aortic dilatation. The results demonstrate that altered wall shear stress in patients regulates biomechanical properties, aortic degeneration, and cell-driven mechanisms. The study identifies a new molecular marker, MYH10, as an indicator of pathological changes in the aortic wall. These findings may be used for the identification of high-risk patients in the future.
“Our research aim is to identify novel molecular targets for aortic dilatation that could be used to develop their therapeutics and diagnostics,” says Academy Research Fellow Johanna Laakkonen of the University of Eastern Finland. “We aim to identify patients with a high risk of aortic dilatation or rupture and improve the follow-up of these patients, thus reducing the risk for life-threatening complications,” says Professor Marja Hedman of the University of Eastern Finland and Kuopio University Hospital.
Source: University of Eastern Finland
15.01.2023