News • Cancer imaging
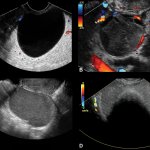
Using ultrasound to predict ovarian cancer
The appearance of ovarian lesions on ultrasound is an effective predictor of cancer risk that can help women avoid unnecessary surgery.

The appearance of ovarian lesions on ultrasound is an effective predictor of cancer risk that can help women avoid unnecessary surgery.

A proof of concept for a robot that can reach some of the smallest bronchial tubes in the lungs to take tissue samples or deliver cancer therapy.

Liquid profiling is offering clear benefits in terms of cancer diagnostics and targeted therapy, but challenges remain in bringing it into the clinic.
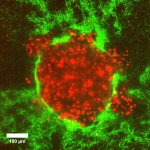
Model tumour systems could help explain whether pressure differences can push cancer cells into their surroundings – a basic mechanism behind metastasis.
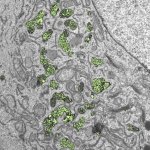
Researchers have succeeded in using metal oxide nanoparticles as "radiosensitizers" – and in producing them on an industrial scale.

Hologic and the Women's Tennis Association (WTA) kicked off a multi-year partnership, launching a joint vision to achieve greater wellness and equality for women.
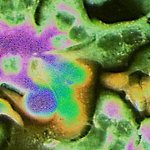
For a long time, the origin of metastasis remained obscure. Now, scientists have discovered some of the mechanisms these cells arise.

Bioengineers have shown they can eradicate advanced-stage ovarian and colorectal cancer in mice in as little as six days with a treatment that could be ready for human clinical trials later this year.
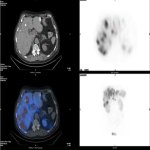
Molecular radiotherapy shows great potential in becoming a more mainstream treatment for cancer, but the field is being hampered by a limited radionuclide supply.
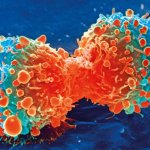
New research from the University of East Anglia (UEA) and Quadram Institute reveals how our immune system can be triggered to attack cancer cells.

A biocompatible ultrasound transducer chip could be a more effective way to harness the technology for biomedical applications.

Mathematical models used as patient surrogates could help clinicians select the best cancer treatment before going to the patient’s bedside.

Researchers have identified a previously unrecognized key player in cancer evolution: clusters of mutations occurring at certain regions of the genome.

Scientists have discovered a means of identifying the risk of breast and ovarian cancer by measuring epigenetic changes in cervical samples from over a thousand women.
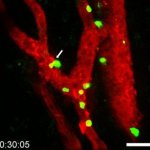
French researchers have found a way to facilitate access to tumours for killer lymphocytes, paving the way for more efficient immunotherapies against cancer.
From solid tumors to metastatic carcinomas and leukemia: cancer is among the most common causes of death. Keep reading for latest developments in early detection, staging, therapy and research.

Scientists at University College London have developed a novel cancer therapy that uses an MRI scanner to guide a magnetic seed through the brain to heat and destroy tumours.

Light therapy may accelerate the healing of skin damage from radiation therapy by up to 50%, according to a recent University at Buffalo-led study.
Faulty versions of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are well known to increase the risk of breast and ovarian cancer. Now, they have been linked to several other cancers, including those that affect men.

Under the roof of integrated diagnostics, radiology, laboratory medicine and pathology are forming a powerful alliance. Hedvig Hricak, MD, PhD, explains the potential for cancer patients and details the role of radiologists within the construct.
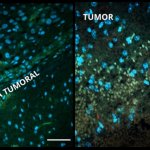
In both the mice and organoids, cytokines suppressed tumor growth after treatment, and defense cells migrated to the brain region affected by the tumor, alerting the immune system to its existence.
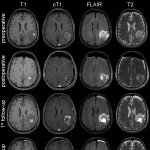
New research has pinpointed ethnicity as a potential factor in brain tumour survival. A UK study showed that white British people who have been diagnosed with a malignant primary brain tumour appear to have an increased one-year mortality than patients from at least four other ethnic groups.
Researchers outline a new minimally invasive and inexpensive blood test that can identify cancer in patients with non-specific symptoms and whether these cancers have metastasised in the body.

Mark Nicholls reports from the National Cancer Research Institute (NCRI) virtual Festival, with four expert speakers discussing the role of liquid biopsy in cancer detection.
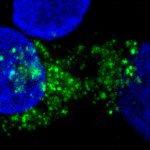
Researchers have identified a mechanism that impairs the proliferation of cancer cells and induces their death without affecting healthy cells. This could lead to improved cancer treatment.