News • Voice pathology detection
Detecting cancer from voice samples: improving the VPD method
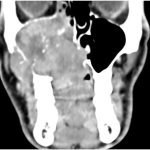
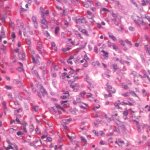
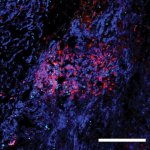
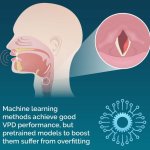
Voice pathology detection (VPD) can detect abnormal vibrations in the vocal cords caused by conditions like cancer and cysts. Now, researchers have found a way to make the method more reliable.