Article • Colon cancer
Revolution and evolution in oncology
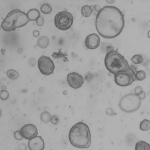
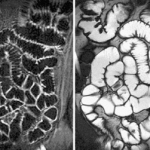
Dr Georg Ralle, General Secretary of the association ‘Network against Colon Cancer’ since 2012 as well as moderator of the symposium ‘The New Measurement of Oncology’, hosted by the National Centre for Tumour Diseases Heidelberg (NCT), clearly voices his dissatisfaction with the German ‘wait it out mentality’. He sharply criticised the Federal Joint Committee (G-BA) and here also…