News • Artificial selection
Improving clinical trial recruitment with AI
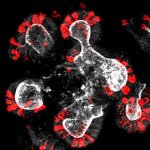
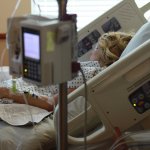
Clinical trials are a critical tool for getting new treatments to people who need them, but research shows that difficulty finding the right volunteer subjects can undermine the effectiveness of these studies. Researchers at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center designed and tested a new computerized solution that used artificial intelligence (AI) to effectively identify eligible…