News • Vaccination
Predicting mRNA degradation to improve vaccine stability
Messenger Ribonucleic Acid (mRNA) as a therapeutic approach is gaining momentum due to its ability to be rapidly manufactured and its promising outcomes.

Messenger Ribonucleic Acid (mRNA) as a therapeutic approach is gaining momentum due to its ability to be rapidly manufactured and its promising outcomes.
US researchers have developed a way to use MRI scanning to map body cell metabolism, opening up new possibilities for detecting cancers and revealing if a tumor is responding to treatment.
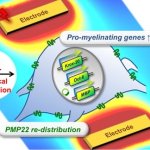
A research team from DGIST develops an electronic medicine technology that restores abnormal protein behavior, the cause of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease (CMT).

A new study has found that nearly 40% of patients over 50 who recognised they had hearing loss did not inform a doctor or nurse, despite the reduced quality of life and associated health risks.

A new study from Finland and Norway shows that babies born preterm are more likely to have asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, COPD, in adulthood.

Among all but oldest age groups, the US has higher death rates than five high-income European nations, according to new UCLA research. However, this gap is only partly due to Covid-19.
A new study led by the University of Edinburgh has identfied areas of the brain susceptible to damage from high blood pressure, affecting memory loss, thinking skills and dementia.

More than 40% of women report anxiety four months after a cardiac arrest compared with 23% of men, according to research presented at ESC Acute CardioVascular Care 2023.

A new kind of smart bandage developed at Caltech may make treatment of chronic wounds - for example caused by diabetes - easier, more effective, and less expensive.

Cambridge researchers have developed a new type of neural implant that could restore limb function to amputees and others who have lost the use of their arms or legs.

UK researchers have shown that misophonia, a condition where those affected show a strong negative reaction to everyday sounds, may affect almost one fifth of the general population.
New research has debunked the idea of an “obesity paradox”, whereby overweight or obese patients with heart failure are less likely to end up in hospital or die than people of normal weight.
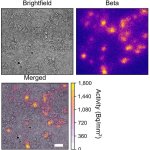
A novel imaging modality that can visualize the distribution of medical radiopharmaceuticals with very fine resolution has been developed and successfully tested.
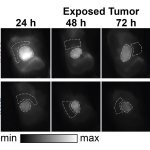
A new real-time imaging technique that uses a type of infrared light has, for the first time, been used during surgery to differentiate between cancerous tumours and healthy tissue.

Do you feel like time sometimes flies, or can drag on when you're bored? A recent study by academics at Royal Holloway shows how our heartbeats can lead to distortions in our perception of time.
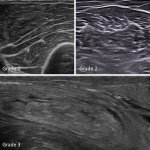
Researchers at the University of Barcelona have developed a new tool to assess the presence and severity of sarcopenia, using an ultrasound-based muscle quality scoring system.
Scientists have discovered why breast cancer cells that have spread to the lungs may ‘wake up’ following years of sleep - forming incurable secondary tumours.
A new study by psychologists at the University of Vienna shows that there is no scientific evidence supporting the alleged positive effect of Mozart's Sonata KV448 on epilepsy.

New research suggests most people don’t understand the difference between a preprint and a published academic journal article. Here is the distinction between the two – and why it is important.

According to Dutch researchers, people with low income are up to 1.5 times more at risk of a heart attack or stroke than their wealthier compatriots. Ethnicity was also identified as a risk factor.
Researchers from the US, Singapore and Geneva have developed a novel combination therapy using an anticancer agent for treating vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis (VRE).
Cancer cells have an innate randomness in their ability to respond to chemotherapy, which is another tool in their arsenal of resisting treatment, new research shows.

Researchers at the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB) have developed a new type of nanoparticles inspired by the structure of amyloids, capable of neutralising the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
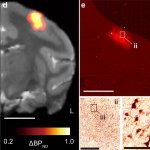
Scientists from Japan demonstrated, for the first time, a successful chemogenetic suppression of widespread epileptic seizures in macaque monkeys. Their findings represent an essential step towards clinical trials, and effective treatment for patients with severe epilepsy.

Researchers at Linköping, Lund, and Gothenburg universities in Sweden have successfully grown electrodes in living tissue using the body’s molecules as triggers.