News • Enabling neuronal tissue growth
A hydrogel to heal the brain
Synthetic hydrogels were shown to provide an effective scaffold for neuronal tissue growth in areas of brain damage, providing a possible approach for brain tissue reconstruction.

Synthetic hydrogels were shown to provide an effective scaffold for neuronal tissue growth in areas of brain damage, providing a possible approach for brain tissue reconstruction.

US researchers are developing a highly accurate machine learning model for early detection of mild cognitive impairment and dementia in older drivers.

Exposure to a mixture of chemicals called PFAS - also known as 'forever chemicals' - leads to alterations in biological processes associated with a broad range of diseases, a new study finds.

Scientists are developing a new kind of light-activated cancer treatments. This would work by switching on LED lights embedded close to a tumour, which would then activate biotherapeutic drugs.

England’s National Child Measurement Programme (NCMP) is designed to tackle childhood obesity. However, a new study suggests it might give rise to mental health problems in children.

Researchers have developed an inhalable powder that could protect lungs and airways from invasion from the coronavirus or flu viruses by reinforcing the body’s own mucosal layer.

Stereotypical gender notions can affect how healthcare staff treat people in pain. This, in turn, may result in medically unjustified disparities in treatment of men and women, or “gender bias.”
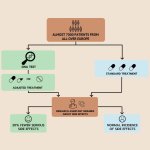
According to an international group of researchers led by Leiden University Medical Center (LUMC), patients experience 30% fewer serious side effects when medication doses are tailored to their DNA.
In a world first, scientists from Singapore and Germany have shown that regenerative therapy to restore impaired kidney function may soon be a possibility.

Experiencing three or more concussions is linked with worsened brain function in later life, according to new research. However, negative effects may already appear after the first injury.

In a promising study, Canadian researchers have shown for the first time in mice that modifying intestinal flora before surgery could reduce postoperative complications in colorectal cancer patients.

Nurses who worked in critical care during the Covid pandemic are at an increased risk of mental health problems, according to a new study.
A Korean research team successfully changed the properties of carcinogenic cells in the lungs and eliminate both drug resistance and their ability to proliferate out to other areas of the body.
A new study from Spain has demonstrated the efficiency of an ultrasound radiation-based therapy on the inhibition of cancer cell motion in pancreas cancer models.

A new approach on the genetic tool CRISPR-Cas9 could reduce the risk of unwanted mutation, making it safer for use in humans, Dutch researchers have found.
High levels of microplastics were detected in surgical environments in a new study. Microplastic was found in both the operating theatre and anaesthetic room, in cardiothoracic surgeries.

Combining single-cell data with a self-learning algorithm reveals how structural changes in chromosomes can trigger cancer. This could pave the way for personalized cancer treatments.
Both high and low dose exercise therapy have beneficial effects in patients with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. However, a new Swedish study shows that, sometime, more can indeed be more.
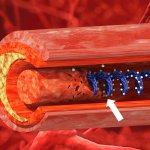
Researchers have developed a new tool and technique that uses “vortex ultrasound” – a sort of ultrasonic tornado – to break down blood clots in the brain.
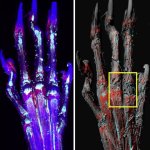
It was previously assumed that bones lacked lymphatic vessels.Now, new research not only locates them within bone tissue, but demonstrates their role in bone and blood cell regeneration.

The European Football Championship in 2021 had an impact on the participating countries' coronavirus infections, a new study shows. However, the extent depended greatly on the initial situation.
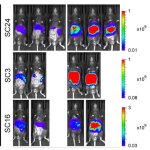
In a new study, researchers from Kanazawa University show how some intestinal cancer cells lose their ability to spread as they divide and can be eliminated as the cancer grows.

Researchers generated human mini bones in the lab which mirror the composition and function of human bone - a step toward the development of future patient-tailored models of bone cancers and tumors.

Monitoring the proper blood supply to the brain could be used to prevent or even treat neurological diseases. A new technique called πNIRS aims to do just that.
For almost four decades, stroke cases and fatalities have been on the decline. In recent years, however, signs point to a resurgence, according to an analysis of US stroke deaths from 1975 to 2019.