News • Potential life-saving bridge
“Artificial lungs” keep patient alive for 48 hours until transplant
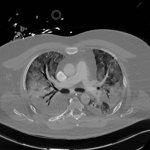
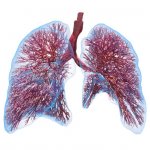
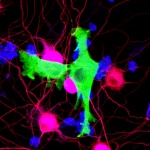
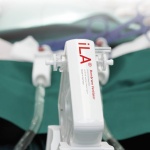
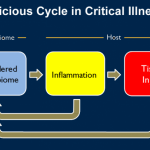
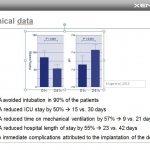
Surviving without lungs for 48 hours: Surgeons describe how they removed a patient’s infected lungs and built “artificial lungs” to keep him alive until a double lung transplant was available.