News • Regenerative properties discovered
Reprogramming immune cells to repair tissue damage
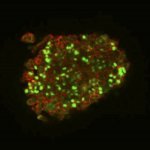
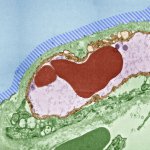
Regulatory T cells (Treg cells) are an immune cell type that reduces excessive immune responses and protects the body against autoimmune diseases. A new study shows that Treg cells in human tissues acquire tissue-regenerative features and describes a method to generate these cells in the laboratory.