News • Lung-brain relationship
Long Covid: researchers track down cause of 'brain fog'
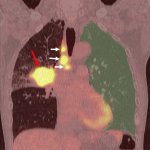
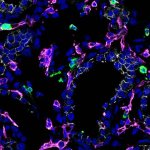
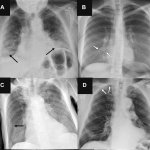
After a Covid-19 infection, patients may suffer from a variety of symptoms, including difficulty concentrating (“brain fog”). New research now linked the condition to impaired lung function.