News • Oncology imaging
‘Digistain’ technology offers revolution in detailed cancer diagnosis
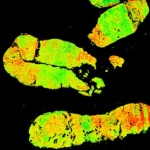
A new imaging technology to grade tumour biopsies has been developed by a team of scientists led by the Department of Physics and the Department of Surgery and Cancer at Imperial College London. Publishing their results in the journal Convergent Science Physical Oncology, they describe how their new method promises to significantly reduce the subjectivity and variability in grading the severity…