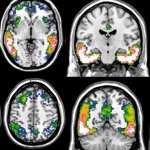
News • Blood-based diagnosis of glioblastoma
Sparing brain cancer patients from undergoing risky surgery
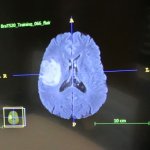
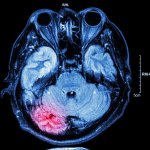
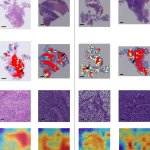
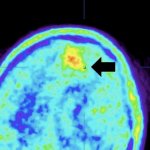
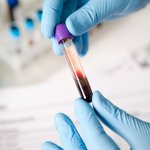
A simple blood test could help diagnose patients with glioblastoma, the deadliest form of brain cancer, sparing them from undergoing invasive and highly-risky surgery, report UK researchers.