
News • Tailored chatbot
Customized ChatGPT to advance digital pathology
New research shows that the AI large language model ChatGPT can be tailored to provide accurate responses to questions about digital pathology and compile detailed results.

New research shows that the AI large language model ChatGPT can be tailored to provide accurate responses to questions about digital pathology and compile detailed results.
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS) often develop into more invasive forms of breast cancer. To predict which DCIS patients are likely to be affected, researchers have developed an analytic AI-based tool.
A new test shows promise in making cervical cancer screening more accessible and less invasive by detecting oncoproteins of the human papillomavirus (HPV) in urine samples.

A new study shows that extracellular vesicles shed by prostate cancer cells contain tumor-derived material that can be used as biomarkers of therapy response and resistance in metastatic disease.

Integrating bacterial genomic data with detailed human mobility data makes it possible to see how pathogens causing pneumonia and meningitis, move between regions and evolve over time.

Researchers have developed an AI model that increases the potential for detecting cancer through sugar analyses. The AI model is faster and better at finding abnormalities than current methods.

A new study describes the outcome of a new approach to testing for Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) guided by the principles of diagnostic stewardship, to help rein in the overtreatment of patients.

A novel blood test shows promise to predict Parkinson's disease in risk patients up to seven years before the typical motor symptoms appear.

Analytical and measurement technology specialist Horiba has expanded its compact hematology instrument range with the launch of new models with Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) on board.
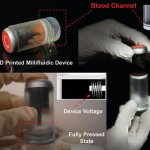
Researchers are proposing a new device that uses blood to generate electricity and measure its conductivity, opening doors to medical care in any location.
Tackling standardization of molecular pathology at a European level remains a major challenge, according to speakers at the 35th European Congress of Pathology in Dublin. One leading expert warned it would be ‘very difficult’ to achieve, though the session also heard about potential solutions such as educational steps to consistently train future pathologists at a high and consistent level.

Acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) is a common type of blood cancer in childhood and can be diagnosed within a few months of life. New research shows that its origins can be traced back to before birth.
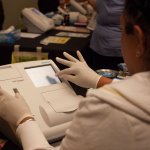
When point-of-care testing (POCT) models for diagnosing infectious disease are effective, the quality of pathology results can be equivalent to laboratory tests, new research shows.

Embark on a journey of unparalleled efficiency and precision with Sakura Finetek Europe's newest innovation in identification technology: the Tissue-Tek xPrint® LP Laser Cassette Printer.
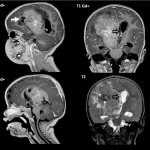
A new study used new molecular analyses to unravel the biological mechanisms of pediatric brain tumors and refine their classification.

A research group established a microfluidic control technology that can be applied to small blood testing devices and consequently developed a novel integrated immunoassay device.

Tissue biopsy and liquid biopsy can increasingly be used as complementary or alternative approaches, with advantages and limitations to each. While speakers at the recent 35th European Congress of Pathology in Dublin were quick to highlight that liquid biopsy was not about to replace tissue biopsy, the focus looked at the benefits and challenges of each through the lens of four expert speakers.

A new study explores the phenomenon of heteroresistance in bacteria, which is a key driver of antibiotic resistance. Two new discoveries could impact the development of future AMR strategies.
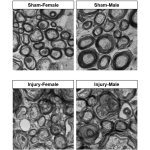
Structural differences in male and female brains might explain why women are more prone to concussions and experience longer recovery from the injury than men, according to a new preclinical study.

Adding a new dimension to pathology: Researchers explore new, deep learning models that can use 3D pathology datasets to make clinical outcome predictions for curated prostate cancer specimens.

A new approach to vaccine development could produce vaccines before the disease-causing pathogen – such as a new variant of the coronavirus Sars-CoV-2 – even emerges.

New research challenges assumptions about the origin of rheumatoid arthritis, which are probably too simple. The findings may point towards improved diagnostics of this painful autoimmune disease.

Blood cancer cells can remain in the blood of AML patients, even after chemotherapy seemed successful. Testing for these residuals before blood cell donation is a vital precaution, a new study finds.
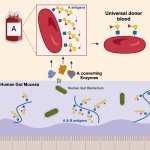
Donor blood is a scarce and valuable resource. Researchers aim to mitigrate this by using enzymes to remove specific sugars that make up the A and B antigens in the human ABO blood groups.

Could the 'gene scissors' CRISPR be used to make resistant bacteria susceptible to first-line antibiotics again? According to new reseach, yes – but the experts also point out serious caveats.