Article • Immersive imaging distraction
VR system to reduce MRI scan anxiety
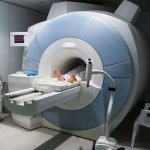
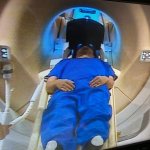
Claustrophobia or anxiety can overwhelm small children and people with cognitive difficulties, especially in a confining and noisy MRI scanner tube. Their restless reactions can then render scan images useless. To help such patients to relax during scanning, a team from King’s College London (KCL) has designed an immersive environment with a special virtual reality (VR) headset for use with MRI…