News • Facing your fear
Google's effect on cancer screening
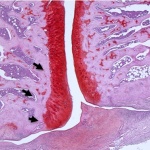
Although modern medicine has made progress in the fight against cancer, the fear of cancer diseases is widespread. Still, regular screenings are no matter of course. Only almost every fifth person over 55 years has undergone a colonoscopy even though it is recommend for this age group as cancer prevention. What influences people to undergo these screenings? Screening or not? In making this…