Article • Creating instruments, implants & more onsite
Reforming surgical procedures with 3D printing hubs in hospitals
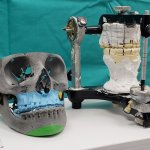
Increasingly, hospitals use 3D printing in surgery because the technology can enable fast, unique production of patient-tailored tools at relatively low costs. ‘As the technology itself is developing and accelerating at a fast pace, hospitals may be left behind if they choose not to adopt these advances,’ said Limor Haviv, surgical 3D printing designer at 3D4OP. Today, 3D printing is used in…