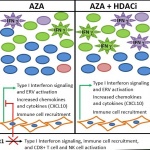
Video • Replicas
Researchers 3D print lifelike artificial organ models
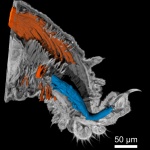
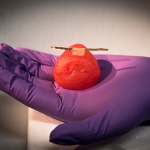
A team of researchers led by the University of Minnesota has 3D printed lifelike artificial organ models that mimic the exact anatomical structure, mechanical properties, and look and feel of real organs. These patient-specific organ models, which include integrated soft sensors, can be used for practice surgeries to improve surgical outcomes in thousands of patients worldwide. “We are…