Sugar processing
Researchers find cellular sweet spot in skin-cancer battle
A team of researchers has pinpointed a sugar modification in cells that spurs the spread of skin cancer. Its findings spotlight a target in the battle against melanoma.

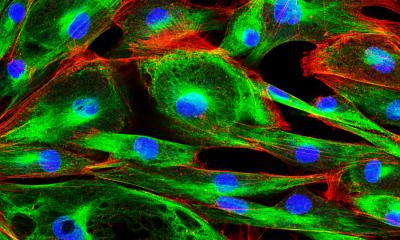
The study reveals that FUT8, an enzyme that transfers the sugar fucose onto proteins, is a driver of melanoma metastasis and, when silenced, suppresses the onset of cancer and the dissemination of tumors in laboratory mice. “This sugar may represent a target for future therapeutic intervention in melanoma,” observes Lara Mahal, a professor in NYU’s Department of Chemistry and one of the paper’s co-authors. The findings, the researchers say, also call for a new, broad-based approach in the hunt for cancer remedies. “There is a clear need to identify new targets and develop innovative drugs that target molecules essential for metastatic melanoma,” notes co-author Eva Hernando, an associate professor of pathology at NYU School of Medicine. “Our results support the value of a systemic approach to identify specific sugars, and related cellular changes, that contribute to melanoma.”
While scientists have long thought that the process in which carbohydrates attach to cells—known as glycosylation—plays an important role in melanoma progression, there are no comprehensive analyses of clinical samples to support this assertion. To address this, the researchers examined more than 30 samples of cancer tissue in patients, focusing on a particular type of glycosylation—fucosylation, or the addition of sugars to a molecule—by FUT8 and other enzymes. Using laboratory mice, the researchers were able to reveal the role of FUT8 in metastasis. In addition, they subsequently focused on the factors behind the spread of melanoma. Here they found that it could be explained by fucosylation by this enzyme. Specifically, their results showed the addition of fucose to a particular molecule, L1CAM, by FUT8 spurred melanoma metastasis. In addition, when this enzyme was silenced, or removed, both the onset and spread of the cancer were stymied.
Source: New York University
14.06.2017