News • At atomic accuracy
Glulisine research could improve diabetes treatment
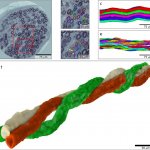
For the first time, scientists have come up with a precise atomic level explanation for why glulisine - a commonly used medication to treat diabetes - is faster acting than insulin. The findings, published in Scientific Reports, could have benefits for diabetes patients in ensuring that a more improved insulin can be developed for future treatment. The study was carried out by experts from the…