News • Subgroup detected
A new Diabetes classification?
The traditional classification of diabetes, mainly in type 1 and type 2 diabetes, has been challenged by studies from Scandinavia.
This is an important step into precision medicine for diabetes and its comorbidities
Michael Roden
In the current issue of The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, researchers from the German Diabetes Center (DDZ) and their partners from the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD) and University of Lund published a cluster analysis of diabetes allowing for phenotyping into subgroups, which extended the findings by showing that risks of certain diabetes-related complications segregated between diabetes subgroups already during the first five years after diagnosis. These results come from the prospective observational multicenter German Diabetes Study (GDS), which follows people with newly diagnosed diabetes for more than 10 years. "The new subgroups will help to develop precise prevention and tailored treatment strategies for the respective high-risk groups," said Professor Michael Roden, principal investigator of GDS and director of DDZ and of the Division of Endocrinology and Diabetology at University Clinics of Düsseldorf. "This is an important step into precision medicine for diabetes and its comorbidities."
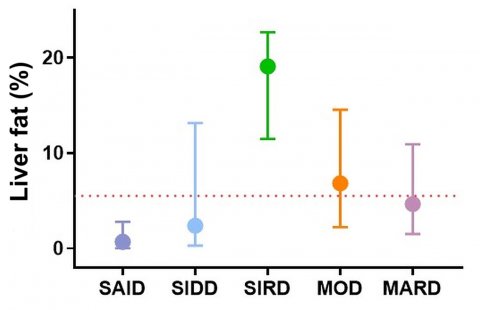
The GDS is conducted at eight locations throughout Germany within DZD, led by DDZ (www.deutsche-diabetes-studie.de). For this analysis, 1105 participants underwent cluster analyses based on the predictive marker GADA (glutamate decarboxylase antibody), age at diagnosis, body mass index (BMI), HbA1c level and HOMA indices (homeostasis model assessment) for insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion. The researchers tested whether comprehensive phenotyping validates and further characterizes these clusters at diagnosis and during follow-up. They also analysed whether relevant complications and comorbidities associated with diabetes, including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), liver fibrosis and diabetic neuropathy, differ among these clusters during the five-year follow-up period. Based on the cluster algorithm, different subgroups with differing risks of complications could be identified: mild age-related diabetes (MARD, 35%), mild obesity-related diabetes (MOD, 29%), severe autoimmune diabetes (SAID, 22%), severe insulin-resistant diabetes (SIRD, 11%) and severe insulin-deficient diabetes (SIDD, 3%). The results show that two subgroups in particular have a high risk of complications. The highest risk of developing non-alcoholic fatty liver was in the cluster of "severe insulin-resistant diabetes" (SIRD); for diabetic neuropathy, the highest risk was in the subgroup "severe insulin-deficient diabetes" (SIDD).
Recommended article
Video • Paradigm shift
Diabetes has 5 subtypes, not 2, study suggests
A completely new classification of diabetes which also predicts the risk of serious complications and provides treatment suggestions. The major difference from today’s classification is that type 2 diabetes actually consists of several subgroups, the results indicate. “This is the first step towards personalised treatment of diabetes”, says physician and diabetes expert Leif Groop.
Conclusion
Using the new diabetes classification, people with type 2 diabetes can be assigned to specific subgroups that exhibit significant metabolic changes and differing risk patterns for the development of diabetes-related complications. Individually targeted prevention and early treatment of specific subgroups of people with diabetes is a step towards precision medicine to delay or even prevent secondary diseases.
Source: German Diabetes Centre (DDZ)
06.08.2019