News • Autoimmune reaction study
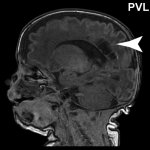
Severe Covid-19 linked to increase in self-attacking antibodies
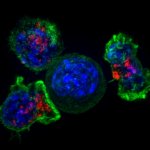
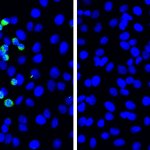
Hospitalized Covid-19 patients are substantially more likely to harbor autoantibodies — antibodies directed at their own tissues or at substances their immune cells secrete into the blood — than people without Covid-19, according to a new study.