
News • Cardiomyopathy research
Genetic defects can cause heart failure
Cardiomyopathy is not a uniform disease. Rather, individual genetic defects lead to heart failure in different ways, an international consortium reports.

Cardiomyopathy is not a uniform disease. Rather, individual genetic defects lead to heart failure in different ways, an international consortium reports.

Researchers have developed adeno-associated virus variants that target heart muscle cells and can thus be used for the precise treatment of heart diseases.
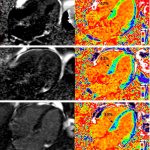
An advanced form of cardiac MRI has for the first-time enabled clinicians to measure the effectiveness of chemotherapy in patients with the life-limiting condition ‘stiff heart syndrome’.

By recreating the helical structure of heart muscles, bioengineers improve understanding of how the heart beats.
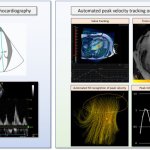
Researchers have developed cutting-edge imaging technology to help doctors better diagnose and monitor patients with heart failure. The state-of-the-art technology uses magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to create detailed 4D flow images of the heart.
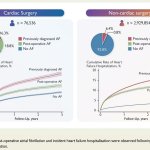
People who develop an abnormal heart rhythm after surgery have an increased risk of subsequently being admitted to hospital with heart failure, according to a study of over 3 million patients.

Artificial intelligence can help diagnose acute heart failure with more accuracy than current blood tests alone, research suggests.

Individuals with diabetes display a substantially increased risk of disease in left-sided heart valves compared to controls without diabetes, a new comprehensive register study shows.

Changes in areas of the brain associated with emotion have been identified in people with Takotsubo syndrome, sometimes known as broken heart syndrome, according to new research.

Researchers have developed a biodegradable gel that can help to improve the delivery of cells into the living heart and could form a new generation of treatments to repair heart attack damage.

Researchers have developed 3D printed artificial heart valves designed to allow a patient’s own cells to form new tissue.

COVID-19 pandemic has caused “global collateral damage” by disrupting cardiac services . Across the world problems with heart health will “...continue to accrue unless mitigation strategies are speedily implemented”.

Wireless bioresorbable pacemaker bypasses need to extract non-biodegradable leads, eliminating additional risk to the patient.

Researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology have developed a smart stent that can monitor hemodynamic parameters. The wireless and battery-free device can transmit the data to the outside of the body.
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI) is a less invasive procedure that is just as effective as open-heart surgery in treating severe symptomatic aortic stenosis, a new study shows.
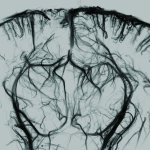
Two successive studies highlight advances in non-invasive 3D ultrasound imaging, making it possible to observe blood flow in real time in the heart and the brain.
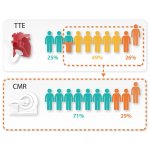
Using MRI scans to detect heart failure could revolutionise how the condition is diagnosed, thanks to new research from the University of East Anglia and the University of Sheffield.

A method for delivering genetic material to the body that has proven useful in Covid-19 vaccination is now being tested as a way to repair damaged heart muscle after a heart attack.

Sleep problems could hint at a heightened risk of heart disease, caution experts at the ESC Preventive Cardiology 2022 congress.
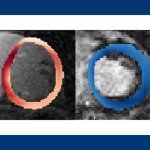
An algorithm built to assess scar patterns in patient heart tissue can predict potentially life-threatening arrhythmias more accurately than doctors can.

For people with atrial fibrillation, one of our most common cardiac disorders, dementia risk is elevated.

Engineers developed a variable stiffness catheter made of nontoxic threads that can transition between soft and rigid states during surgery.
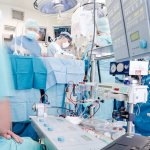
Reducing inflammatory mediators in the blood before surgical treatment of cardiac bacterial infection does not improve clinically relevant outcome, a new study shows.

Smart textiles with built-in sensors and transmitters present themselves as a diagnostic solution as they can monitor heart rhythm over long periods and thus pick up on potential Atrial Fibrillation.
A way to replicate what happens inside the heart after cardiac arrest could open new avenues for the study of heart regeneration whilst reducing the use of live animals in research.