News • Cancer treatment
Immunotherapy approach 'points' killer cells towards tumours
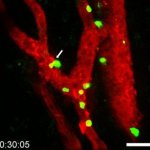
French researchers have found a way to facilitate access to tumours for killer lymphocytes, paving the way for more efficient immunotherapies against cancer.

French researchers have found a way to facilitate access to tumours for killer lymphocytes, paving the way for more efficient immunotherapies against cancer.
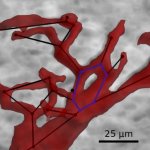
Using a new x-ray imaging approach, an interdisciplinary research team has detected significant changes in the heart muscle tissue of people who died from Covid-19.

A novel protein regulator of tumor angiogenesis, TMEM230, was recently characterized by researchers to have a role in tumor development and vascularization, with potential as a target for anti-tumor therapy in difficult-to-treat cancers such as glioblastoma.
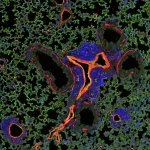
Scientists from the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) and the Medical Faculty Mannheim, Heidelberg University, have identified a new growth factor produced by blood vessels that enables tumor cells to metastatically colonize organs.
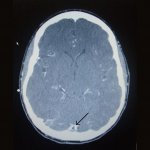
A new study of patients with cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT) following Covid-19 vaccination provides a clearer guide for clinicians trying to diagnose and treat patients. The research, led by University College London (UCL) and UCL Health and published in The Lancet, is the most detailed account of the characteristics of CVT, when it is caused by the novel condition vaccine-induced immune…
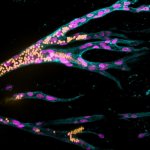
Using lab-created tissue to heal or replace damaged organs is one of the great visions for the future of medicine. Synthetic materials could be suitable as scaffolding for tissue because, unlike natural tissues, they remain stable in the organism long enough for the body to form new natural structures. A fundamental requirement for functional tissue is that blood vessels must be able to grow in…
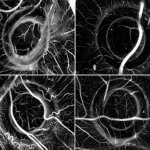
Magnetic fields can be used to stimulate blood vessel growth, according to a new study. The findings, published in the journal Science and Technology of Advanced Materials by researchers at the Técnico Lisboa and NOVA School of Science and Technology in Portugal, could lead to new treatments for cancers and help regenerate tissues that have lost their blood supply.
For the first time, a prospective, international study has shown that chest pain caused by problems with the very small vessels supplying blood to the heart is an important health problem that increases the risk of heart attacks, stroke and death due to cardiovascular reasons. The study, which is published in the European Heart Journal, recruited 686 patients from 14 institutions in seven…
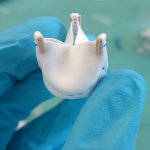
Non-degradable prostheses for cardiovascular tissues can be used to replace heart valves and blood vessels, but they can’t stay in the body permanently. In two recent papers, researchers at the Eindhoven University of Technology (TU/e) in collaboration with a number of clinical partners, the Dutch Heart Foundation, and TU/e spin-off companies Suprapolix, Xeltis, and STENTiT have shown how…

The VeinViewer® uses harmless near-infrared (NIR) light which is directed towards the patient’s skin. Haemoglobin in the blood absorbs the NIR and the surrounding tissue reflects it back to the VeinViewer® device, where the data is processed into an image, colour is added and the image sent back to the skin to provide a real time visualization of the blood vessels and patterns up to 10mm…

Biomedical engineering researchers at Texas A&M University designed a medical device that mimics blood vessels to design and monitor drugs for patients with clotting disorders. This approach could be especially beneficial for pediatric patients. Unlike what a biology textbook may show, blood vessels are not straight cylinders. They are tortuous, meaning they have complex curves, spirals and…
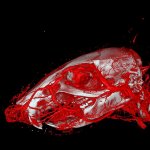
Researchers at the University of Zurich have developed a new X-ray contrast agent which is easier to use and distributes into all blood vessels more reliably, increasing the precision of vascular imaging. This reduces the number of animals required in research experiments. Various diseases in humans and animals – such as tumors, strokes or chronic kidney disease – damage the blood vessels.…
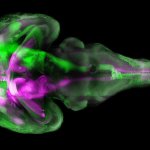
Diseases of the brain are often associated with typical vascular changes. Now, scientists at LMU University Hospital Munich, Helmholtz Research Centre for Environmental Health and the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have come up with a technique for visualising the structures of all the brain's blood vessels – right down to the finest capillaries – including any pathological changes. So…

Scientists of Jena University Hospital, Germany, conducted a meta-analysis to evaluate benefit and risk of paclitaxel-coated balloon angioplasty compared to conventional balloon angioplasty as therapy of intermittent claudication. The study confirms an increased all-cause mortality, which has formerly been stated, and found a broad heterogeneity in the effectivity of the procedure depending on…
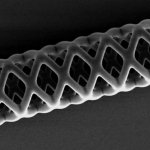
Researchers at ETH Zurich have developed a new method for producing malleable microstructures – for instance, vascular stents that are 40 times smaller than previously possible. In the future, such stents could be used to help to widen life-threatening constrictions of the urinary tract in foetuses in the womb. Approximately one in every thousand children develops a urethral stricture,…
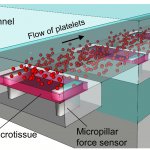
Blood clotting is one of the most critical, protective processes in human physiology. When something goes wrong with clotting, either because there is too much clotting, leading to a stroke, or not enough, leading to internal bleeding, the outcome can be catastrophic. Now, University at Buffalo researchers have established an in vitro model of this process that will help clinicians improve…
Researchers in the Medical Sciences Division of Oxford University have established a key cause of micro blood vessels constricting during surgery to reopen a blocked artery, and identified a potential therapeutic target to block the mechanism behind it. During the emergency procedure used to reopen the blocked artery causing a heart attack, smaller "micro" blood vessels can remain…
Researchers have discovered that a family of lipids (fats) contribute to the development of a serious aortic disease, by driving clotting in the blood vessel wall. The findings could lead to the development of new treatments for this potentially life threatening condition. The team, led by researchers at Cardiff University, in collaboration with colleagues at Oxford and Erlangen, discovered that…
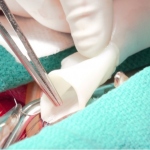
In a groundbreaking new study led by University of Minnesota biomedical engineers, artificial blood vessels bioengineered in the lab and implanted in young lambs are capable of growth within the recipient. If confirmed in humans, these new vessel grafts would prevent the need for repeated surgeries in some children with congenital heart defects.

EPIC Alliance experts at the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) congress presented original research and real-world clinical evidence on non-responders to cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) and atrial fibrillation (AF) ablation.
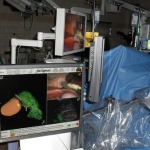
In addition the technique to grow the blood vessels in a 3D scaffold cuts down on the risk of transplant rejection because it uses cells from the patient. It was developed by researchers from the University of Bath's Department of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, working with colleagues at Bristol Heart Institute.
For the examination of coronary blood vessels, intravascular methods with imaging technologies are already state-of-the-art. However, ultrasonic methods, which are used to gather information about the tissue, can only be used externally, up to now. The piezo electronical components necessary for this have not been sufficiently miniaturized to be inserted into the blood vessels.
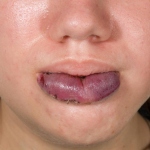
A drug currently being trialled in cancer patients could also be used to treat an often incurable condition that can cause painful blood vessel overgrowths inside the skin, finds new research in mice led by UCL, Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK) Cancer Center in New York and the Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBELL) in Barcelona.
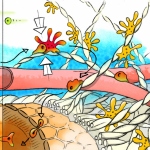
A research team headed by scientists at the Institute of Neuroimmunology and the Institute for Multiple Sclerosis Research (IMSF), University Medical Center Göttingen (UMG), has gained new insights into the immune function of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). They used real-time microscopy to film the lively trafficking of immune cells between the CSF and the nervous tissue. Here the meninges play the…