Sponsored • Periprosthetic protection
Bone cements containing antibiotics for infection prophylaxis – quo vadis?
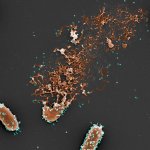
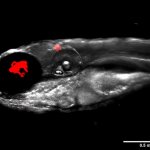
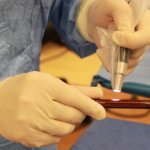
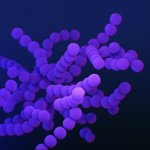
Periprosthetic infections and revisions are on the rise in Germany and worldwide, with significant consequences for affected patients as well as for the healthcare systems. Precisely because the number of patients at higher risk of infection in arthroplasty continues to rise, attention is increasingly focused on how this dreaded complication can be avoided.