News • Electronic prompt in the EHR
‘Nudging’ surgeons away from breast cancer overtreatment
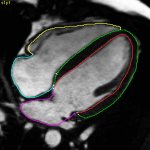
Sentinel lymph node biopsies can help detect breast cancer – but not every patient benefits from the procedure. New research finds that a simple EHR prompt can prevent unnecessary surgery.