News • New insights on CLEC5A
Immune gene discovery could prevent memory loss in Alzheimer's patients
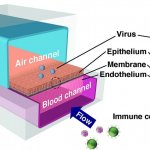
A gene once believed to fight only viral infections could also hold the key to preventing memory loss in Alzheimer’s patients, a new study finds. This paves the way for new drug developments.