News • Children’s cancer
Rhabdomyosarcoma: Blood tests could offer smarter treatment
A simple 'liquid biopsy' blood test could help guide the treatment of children with the cancer rhabdomyosarcoma, a new study reports.

A simple 'liquid biopsy' blood test could help guide the treatment of children with the cancer rhabdomyosarcoma, a new study reports.
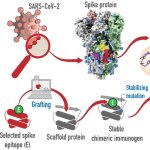
A vaccine design approach that could protect against new variants of SARS-CoV-2 but also potentially protects against other coronaviruses is one step closer to reality as a result of new research.

In a survey of emergency department staff from across Europe, only around half said their hospital has a policy in place to help staff identify children who are being neglected or abused.
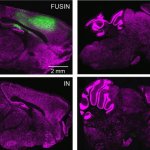
Treatment of central nervous system diseases and tumors is often hindered by the blood-brain barrier. A new method aims to overcome this obstacle using focused ultrasound intranasal delivery (FUSIN).

Many women diagnosed with breast cancer can be cured with surgery, radiotherapy and medical treatment. Swedish researchers explore whether physical exercise can support the anti-tumour effects.

Methamphetamines, cocaine, opiates, and cannabis are associated with an increased likelihood of developing atrial fibrillation, a newly-published 11-year study shows.

Covid-19 has led to global mortality changes unprecedented in the last 70 years, according to new research. However, the drop in life expectancy is not equally high in all countries.

Routine sampling of water supplies and genomic sequencing of Legionella bacteria could play a key role in identifying the source of Legionnaires’ disease outbreaks, research suggests.
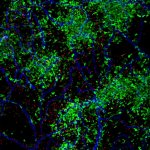
Researchers mapped in detail how the immune system acts against pathogens invading the brain. This sheds new light on host-pathogen interactions and the long-term consequences of brain infections.

Not just uncomfortable, but hard on the heart: Accumulating research suggests a link between hot flashes during the menopause and cardiovascular disease risk in women.

Researchers in Munich have developed a novel model system that can be used to precisely track the growth steps and three-dimensional arrangement of pancreatic cancer cells.

Researchers have shown that when brain cells are directly exposed to blood taken from Covid-19 patients with delirium, there is an increase in cell death and a decrease in the generation of new brain cells.
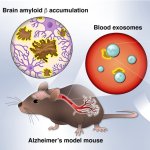
Researchers from Japan have developed a method to detect build-up of amyloid β in the brain, a characteristic of Alzheimer’s disease, from biomarkers in blood samples.
Scientists in Italy discovered a new drug-resistance mechanism in breast cancer that leads to the formation of cancer stem cells. They also devised an experimental therapy to bypass or prevent this.
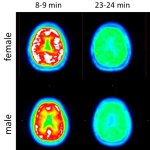
US researchers have developed a test to detect loss of myelin - a key contributor to many neurological diseases including multiple sclerosis, traumatic brain and spinal cord injuries, stroke, and dementia.

Researchers at Lund University in Sweden and Skåne University Hospital have conducted an animal study bringing hope that more donor lungs could be used in the future.
A research team has investigated how contrast agents disperse inside cells. This could improve the assessment and further development of these agents and contribute to future medical diagnostics.
Cambridge scientists have discovered that cancer cells ‘hijack’ a process used by healthy cells to spread around the body, completely changing current ways of thinking around cancer metastasis.

A newly developed capsule that tunnels through mucus in the GI tract could be used to orally administer large protein drugs such as insulin.

A research group has revealed that SARS-CoV-2 disrupts the vascular endothelial barrier by suppressing the expression of Claudin-5 (CLDN5) to invade the blood vessels.

A new device for diagnosing bone fragility invented by the University Hospitals of Geneva (HUG) and the University of Geneva (UNIGE) has been approved for marketing in the European Economic Area and Switzerland. The device is based on a new approach to assessing bone quality via blood sampling.
As the monkeypox outbreak continues to spread around the globe, a rare but potentially serious complication of the virus has been discovered.

The oncogene EVI1 causes an aggressive type of leukemia, but its exact function has been a mystery. A research team now showed that EVI1's cancer causing effect relies on activating a single gene — the stem cell transcription factor ERG.

Women can suffer for years with the debilitating pain and medical complications of endometriosis without a diagnosis. Now, researchers believe they may be able to diagnose the condition using just menstrual blood.
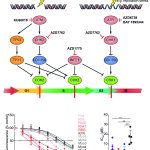
Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is a rare pediatric tumor. For more than 40 years there has not been any new development regarding treatment. Research led by Prof. Dr. Anton Henssen at Charité University Berlin has now identified a new therapeutic option, using a drug that is currently under investigation for other types of cancer.