News • Oncology
Pancreatic cancer: Enzyme renders tumors resistant
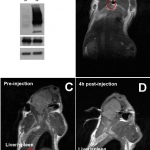
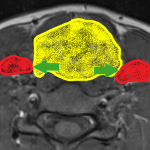
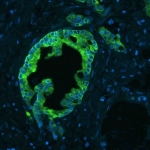
Scientists at the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) and the Stem Cell Institute HI-STEM in Heidelberg have discovered the reason why some pancreatic tumors are so resistant to treatment. They have found that these tumor cells produce larger quantities of an enzyme that usually occurs in the liver and degrades many drugs. If this enzyme is blocked, the cancer cells become sensitive towards…