News • Protein aggregation
Parkinson's: Why copper could make it worse
Copper exposure in the environment and the protein alpha-synuclein in the human brain could play an important role in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease, researchers found.

Copper exposure in the environment and the protein alpha-synuclein in the human brain could play an important role in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease, researchers found.
The classification of brain tumors—and thus the choice of optimal treatment options—can become more accurate and precise through the use of artificial intelligence in combination with physiological imaging.
When every minute counts: A Swiss team is currently developing a diagnostic procedure that can be used to start a tailored therapy for acute stroke in a timely manner.

Changes in areas of the brain associated with emotion have been identified in people with Takotsubo syndrome, sometimes known as broken heart syndrome, according to new research.
Researchers have shown that aggregation of amyloid-beta, one of two key proteins implicated in Alzheimer’s disease, causes cells to overheat and ‘fry like eggs.’
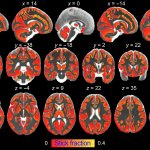
Researchers visualize brain inflammation using diffusion-weighted MRI. This detailed "X-ray" of inflammation cannot be obtained with conventional MRI, but requires data acquisition sequences and special mathematical models.

A new way of differentiating healthy from diseased cells could pave the way for more personalised treatment for patients diagnosed with glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), a common and aggressive type of brain tumour.
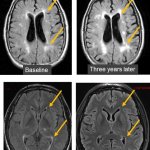
Cerebral white matter hyperintensities (WMH) can have a devastating impact on a patient’s life. Radiologists must learn to recognise these white spots in the brain and conventional imaging may just reveal the tip of the iceberg.

A research team in Spain and the US has created 3D-printed acoustic holograms to improve the treatment of diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, among others.
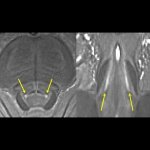
Ultra-powerful 7T MRI scanners could be used to help identify patients with Parkinson’s disease and similar conditions who are most likely to benefit from new treatments, say scientists.
Swiss researchers discovered how different cell types in cortex change their activity during general anesthesia, helping to understand how unconsciousness may be induced.
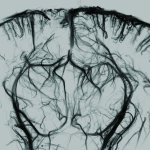
Two successive studies highlight advances in non-invasive 3D ultrasound imaging, making it possible to observe blood flow in real time in the heart and the brain.
Dr Christina Malamateniou spoke to The European Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine and Biology about the recent review she led to help make MRI brain scans more accessible to autistic people.

Cognitive impairment as a result of severe Covid-19 is similar to that sustained between 50 and 70 years of age and is the equivalent to losing 10 IQ points, scientists found.
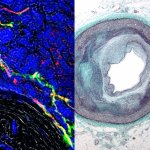
An international team has for the first time demonstrated that nerve signals are exchanged between clogged up arteries and the brain.
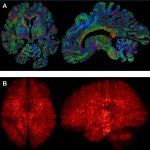
A team led by scientists from Amsterdam have combined MRI and microscopy to produce 3D images of two entire brains with a previously unmatched level of detail.
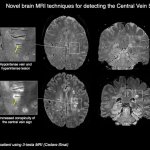
Cedars-Sinai physician-scientists are pioneering imaging techniques and investigating new biomarkers to improve multiple sclerosis (MS) diagnosis and treatment.
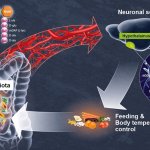
Hypothalamic neurons in an animal model directly detect variations in bacterial activity and adapt appetite and body temperature accordingly.

Engineers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have developed a telerobotic system to help surgeons quickly and remotely treat patients experiencing a stroke or aneurysm.
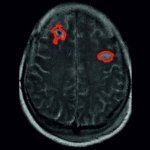
Researchers from Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin have shown that massive electrochemical waves in the brain act as a marker announcing an impending ischemic stroke.
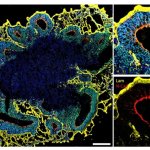
Scientists use miniature brain models to understand how a mutated gene affects brain development.

For people with atrial fibrillation, one of our most common cardiac disorders, dementia risk is elevated.

Can mobile phones increase the risk of brain cancer? A new, large study was unable to verify such concerns. However, the researchers say it might still be a good idea to cut back on smartphone time.

Scientists are developing a novel method for treating brain haemorrhages which it is hoped could reduce the risk of brain damage and disability and increase patients’ chances of survival.

A wireless sensor could offer doctors a way to monitor changes in brain chemistry without requiring a second operation to remove the implant.