News • PET imaging
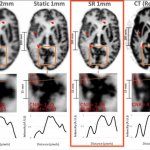
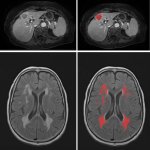
Super-resolution enables detailed brain imaging
A new imaging technique has the potential to detect neurological disorders at their earliest stages, enabling physicians to diagnose and treat patients more quickly.

A new imaging technique has the potential to detect neurological disorders at their earliest stages, enabling physicians to diagnose and treat patients more quickly.

Research teams from TU Darmstadt, British and US universities are focusing on one possible main process that leads to the death of brain cells in their investigation of the causes and mechanisms of Alzheimer's disease.

Neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and epilepsy have had some treatment success with deep brain stimulation, but those require surgical device implantation. A multidisciplinary team at Washington University in St. Louis has developed a new brain stimulation technique using focused ultrasound that is able to turn specific types of neurons in the brain on and off and precisely…

Brown University researchers have developed a technique that could allow deep brain stimulation devices to sense activity in the brain and adjust stimulation accordingly.
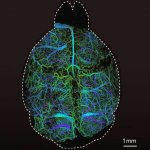
Researchers from ETH Zurich and University of Zurich have developed a new microscopy technique that lights up the brain with high resolution imagery. This allows neuroscientists to study brain functions and ailments more closely and non-invasively.

Two clusters of brain cells compete to promote either the persistence or disappearance of traumatic memories, according to a new study conducted in mice. The findings could provide important insights into human conditions such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety disorders, and associated problems such as alcohol use disorder (AUD) that can arise from the persistence of traumatic…
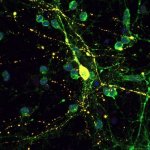
A new idea for treating Alzheimer’s disease could eradicate the toxic proteins most closely linked to cognitive decline in the places where they do the most damage, a study from researchers at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons suggests. The study was published online in Science Translational Medicine.
Researchers from Case Western Reserve University have identified a potential new approach to better controlling epilepsy. Lin Mei, professor and chair of the Department of Neurosciences at Case Western Reserve School of Medicine, who led the new study in mouse models, said the team found a new chemical reaction that could help control epileptic seizures.

Thin-film electrodes developed at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have been used in human patients at the University of California, San Francisco, generating never-before-seen recordings of brain activity in the hippocampus, a region responsible for memory and other cognitive functions. In a study published in the journal Nature Communications, surgeons at UCSF placed the flexible…
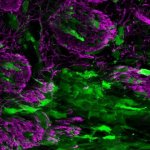
Scientists at the University College London (UCL) have made a ‘surprising’ discovery that glioblastoma, an aggressive brain cancer, mimics normal brain repair in white matter, which leads to the tumour becoming less malignant. In the study on mice, funded by Cancer Research UK and published in Nature Communications, researchers used these novel findings to identify drugs which could be used,…
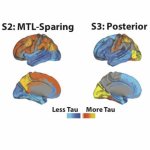
Alzheimer's disease is characterized by the abnormal accumulation and spread of the tau protein in the brain. An international study can now show how tau spreads according to four distinct patterns that lead to different symptoms with different prognoses of the affected individuals. The study was published in Nature Medicine.

A new photonics device currently in development aims to reduce unnecessary disabilities by improving the instant, real-time monitoring of newborn babies with harmless light particles.
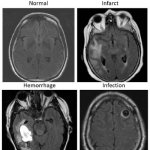
An artificial intelligence (AI)-driven system that automatically combs through brain MRIs for abnormalities could speed care to those who need it most, according to a new study. “There are an increasing number of MRIs that are performed, not only in the hospital but also for outpatients, so there is a real need to improve radiology workflow,” said study co-lead author Romane Gauriau, PhD,…
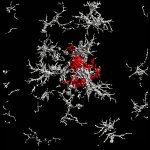
One of the characteristic hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the buildup of amyloid-beta plaques in the brain. Most therapies designed to treat AD target these plaques, but they’ve largely failed in clinical trials. New research by scientists at the Salk Institute upends conventional views of the origin of one prevalent type of plaque, indicating a reason why treatments have been…
Researchers at the University of Oxford report that the risk of the rare blood clotting known as cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT) following Covid-19 infection is around 100 times greater than normal, several times higher than it is post-vaccination or following influenza. The study authors, led by Professor Paul Harrison and Dr Maxime Taquet from Oxford University’s Department of Psychiatry and…
At a cost of $38 billion a year, an estimated 5.3 million people are living with a permanent disability related to traumatic brain injury (TBI) in the United States today, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The physical, mental and financial toll of a TBI can be enormous, but new research from the University of Georgia provides promise. In a new study, researchers at…
Tumor vaccines can help the body fight cancer. Mutations in the tumor genome often lead to protein changes that are typical of cancer. A vaccine can alert the patients' immune system to these mutated proteins. For the first time, physicians and cancer researchers from Heidelberg and Mannheim have now carried out a clinical trial to test a mutation-specific vaccine against malignant brain tumors.…
Alzheimer’s disease seems to progress faster in women than in men. The protein tau accumulates at a higher rate in women, according to research from Lund University in Sweden. The study was recently published in Brain. Over 30 million people suffer from Alzheimer’s disease worldwide, making it the most common form of dementia. Tau and beta-amyloid are two proteins known to aggregate and…

Due to their tissue-like mechanical properties, hydrogels are being increasingly used for biomedical applications; a well-known example are soft contact lenses. These gel-like polymers consist of 90 percent water, are elastic and particularly biocompatible. Hydrogels that are also electrically conductive allow additional fields of application, for example in the transmission of electrical signals…

The German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE) and Eisai Co., Ltd. announced that both parties have entered into a research collaboration agreement aiming to create potential novel treatments for neurodegenerative disorders including Alzheimer’s disease (AD) which modulate immune competence in neurons and glia cells.
AI is revamping workflows and experts showed how radiologists can integrate it into their department to improve daily practice and healthcare at ECR. The panel also discussed the health economics side of AI to help radiologists define which products make more economic sense for their department. The session tackled automated organ segmentation, an interesting application for AI in radiology.
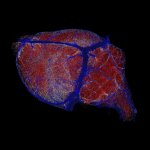
Our brains are non-stop consumers. A labyrinth of blood vessels, stacked end-to-end comparable in length to the distance from San Diego to Berkeley, ensures a continuous flow of oxygen and sugar to keep our brains functioning at peak levels. But how does this intricate system ensure that more active parts of the brain receive enough nourishment versus less demanding areas? That’s a century-old…

Grafting neurons grown from monkeys’ own cells into their brains relieved the debilitating movement and depression symptoms associated with Parkinson’s disease, researchers at the University of Wisconsin–Madison report. In a study published in the journal Nature Medicine, the team describes its success with neurons made from induced pluripotent stem cells from the monkeys’ own bodies.…

Researchers at the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona obtained a highly accurate recreation of human glioblastoma’s features using a novel 3D microscopy analysis. The study, published in the journal Acta Neuropathologica Communications, provides new information to help with the diagnose, by finding therapeutical targets and designing immunotherapeutical strategies.
Prolonged anesthesia, also known as medically induced coma, is a life-saving procedure carried out across the globe on millions of patients in intensive medical care units every year. But following prolonged anesthesia--which takes the brain to a state of deep unconsciousness beyond short-term anesthesia for surgical procedures--it is common for family members to report that after hospital…