News • Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy imaging
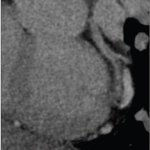
Combining cDTI and CMR to detect deadly heart condition
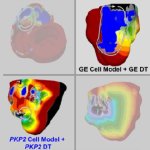
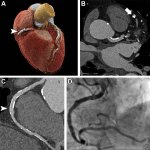
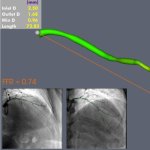
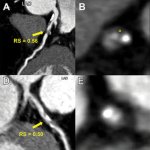
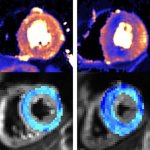
Combining two types of heart scan techniques could help doctors to detect deadly hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) before symptoms and signs on conventional tests appear.