News • Nice catch
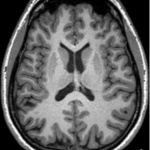
Eating fish may reduce risk of MS
Eating fish at least once a week or eating fish one to three times per month in addition to taking daily fish oil supplements may be associated with a reduced risk of multiple sclerosis (MS), according to a preliminary study that will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology’s 70th Annual Meeting in Los Angeles, April 21 to 27, 2018. These findings suggest that the omega-3 fatty acids…