Article • Combatting infections
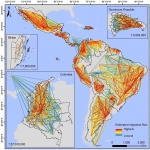
The global migration mapping project
Experts at a university in the United Kingdom have designed a large-scale data and mapping project that they hope will help in the global fight against infectious diseases.

Experts at a university in the United Kingdom have designed a large-scale data and mapping project that they hope will help in the global fight against infectious diseases.
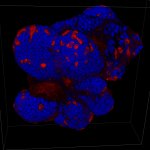
Professor Hans Clevers, researcher and group leader at the Hubrecht Institute in Utrecht, the Netherlands, invented the organoids, a ground-breaking new technique to grow new ‘organs’ and to test medication.
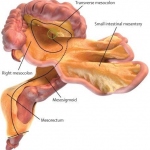
University of Limerick professor J Calvin Coffey has identified an emerging area of science having reclassified part of the digestive system as an organ.
An international team of 56 researchers in five countries has confirmed a hypothesis first proposed by the ancient Greeks – that different diseases are characterized by different “chemical signatures” identifiable in breath samples. The findings by the team led by Professor Hossam Haick of the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology Department of Chemical Engineering and Russell Berrie…

Curetis N.V. and the European Investment Bank (EIB) today announced that the EIB granted Curetis a EUR 25 million senior, unsecured loan. The financing is the first growth capital loan under the European Growth Finance Facility (EGFF). It is backed by a guarantee from the European Fund for Strategic Investments (EFSI).

An analysis of 2,000-year-old human remains from several regions across the Italian peninsula has confirmed the presence of malaria during the Roman Empire, addressing a longstanding debate about its pervasiveness in this ancient civilization.
SCIEX’s donation to the WCRF following several significant research partnerships with world-leading cancer scientists to advance the promise of Precision Medicine.
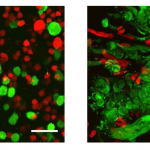
3-D printed tumour-like constructs will be used by a research team at Scotland’s Heriot-Watt University in Edinburgh, to raise research to a new level and successfully lead to new treatment options.
In Europe, the first baby with Zika-related microcephaly was born in July. The mother had contracted the Zika virus while travelling in America. How dangerous is the virus for Europeans, particularly since many visited Brazil for the Olympic Games in Rio?

Airports are international travel hubs visited by large numbers of people. London Heathrow, for example, has an average of 205,400 travellers every day and saw 75 million people arriving and departing from all over the world in 2015. A study just published in the journal Clinical Microbiology and Infection suggest that international travellers can acquire antimicrobial-resistant bacteria and may…

Our knowledge of causes and mechanisms of current and future diseases is on ice – not the perpetual ice of the polar caps but artificial ice. It is stored in biobanks at -80 to -160 °C.
A new study by Johns Hopkins researchers suggests that a specialized area of the mosquito brain mixes tastes with smells to create unique and preferred flavors. The findings advance the possibility, they say, of identifying a substance that makes “human flavor” repulsive to the malaria-bearing species of the mosquitoes, so instead of feasting on us, they keep the disease to themselves,…
This week, The BMJ launches a new series called ‘Rapid Recommendations,’ a collaboration with an international group of researchers and doctors, working together with patients, to quickly and reliably transform research evidence into clinical practice recommendations.
Malaria remains one of the world’s leading causes of mortality in developing countries. Last year alone, it killed more than 400,000 people, mostly young children. An international consortium of researchers unveiled the mechanics and findings of a unique “open science” project for malaria drug discovery that has been five years in the making.
Researchers have found that Zika virus can live in eyes and have identified genetic material from the virus in tears, according to a study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. The research, in mice, helps explain why some Zika patients develop eye disease, including a condition known as uveitis that can lead to permanent vision loss.
There are a couple strains of herpes so common that researchers estimate 90% of the human population have them. These strains, human herpes 6 and human herpes 7, usually do not cause severe symptoms when people acquire them. But researchers know that under certain circumstances, dormant herpes viruses in the body can unexpectedly come roaring back and cause complications not typically associated…
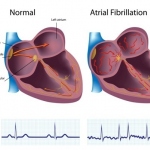
Two new studies have focused on the impact of weekend care and discharge on heart patients within the NHS in England. In one, patients suffering atrial fibrillation (AF) who were admitted to a National Health Service (NHS) hospital over the weekend faced a higher risk of dying within five years than patients admitted during normal hours.

Osnabrueck cognitive scientists and their students are developing new and intelligent expert systems, which help to effectively utilize the flood of daily information in everyday life. To enable working with large amounts of data, the Institute of Cognitive Science at Osnabrück University has engaged in a cooperation with the global corporation IBM, and will be able to access the IBM computer…
A study published by The BMJ provides more details of an association between Zika virus infection in the womb and a condition known as arthrogryposis, which causes joint deformities at birth, particularly in the arms and legs.
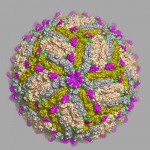
Scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have identified antibodies capable of protecting against Zika virus infection, a significant step toward developing a vaccine, better diagnostic tests and possibly new antibody-based therapies. The work, in mice, helps clarify recent research that also identified protective Zika antibodies but lacked important details on how the…
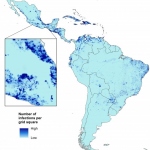
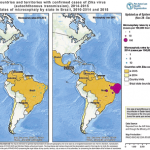
Research by scientists in the US and UK has estimated that up to 1.65 million childbearing women in Central and South America could become infected by the Zika virus by the end of the first wave of the epidemic. Researchers from the WorldPop Project and Flowminder Foundation at the University of Southampton and colleagues from the University of Notre Dame and University of Oxford have also found…
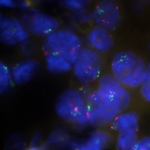
The Ligand PD-L1 is one of the most important targets for cancer immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors. But not all tumors have sufficient quantities of PD-L1 ligands on their surface. Scientists from the German Cancer Consortium (DKTK) have now shown that different types of cancer possess different quantities of PD-L1-Gen copies. Genetic analysis of the PD-L1 gene may in the future help to…
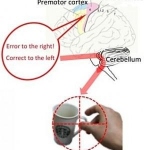
Adaptation in reaching - gradual improvement of motor control in response to a perturbation - is a central issue in motor neuroscience.However, even the cortical origin of errors that drive adaptation has remained elusive. In a new paper Inoue, Uchimura and Kitazawa have shown that error signals encoded by motor cortical neurons drive adaptation in reaching.
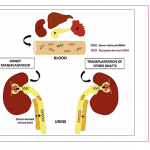
As part of a national, joint research project in cooperation with Chronix Biomedical (San Jose, CA/USA/Göttingen/Germany), Professor Michael Oellerich MD is on new biomarkers in organ transplantation, aiming to develop personalised immunosuppression for patients. This also entails the development of molecular test procedures, among others for the early detection of rejection. The keyword here is…
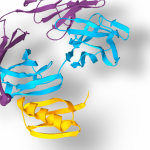
Many drug treatments do not work due to their poor ability to reach their intended targets inside patients’ cells. To address this, researchers at Cardiff University’s Schools of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, and Biosciences have designed a highly efficient method to improve the delivery of therapeutic molecules into diseased cells such as those in stomach cancer, breast cancer and…