Article • Standards
We expect to see some changes
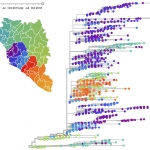
Strictly speaking, digital pathology has not yet resulted in any groundbreaking changes for clinical diagnostics. The conventional light microscope introduced to pathology around 100 years ago continues to be the most important tool for pathologists.