Sponsored • Brachytherapy in LAPC patients
Innovative Avenue of Treatment – Internal Radiotherapy for Locally Advanced Unresectable Pancreatic Cancer
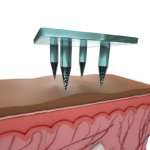
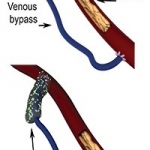
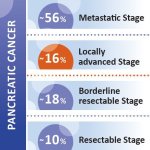
In more than one in six patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancer, the tumour is initially diagnosed at a non-metastatic primarily unresectable, locally advanced stage (LAPC). For these patients, a new internal radiation procedure, OncoSil™ brachytherapy, may become a treatment option – in Germany, around 858 patients could benefit from this innovation annually.