News • Neurodegenerative diseases
Tauopathy or Alzheimer's? Biomarker and PET imaging for improved diagnosis
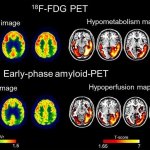
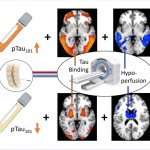
Researchers have identified biomarkers that, in conjunction with PET imaging, enable doctors to reliably distinguish between primary 4-repeat tauopathies and Alzheimer's disease.